KUALA LUMPUR, 31 October 2025: International air passenger traffic continues to scale up according to the Preliminary September 2025 traffic figures released Thursday by the Association of Asia Pacific Airlines.
APPA data shows resilient regional economic conditions, underpinned by Asia Pacific GDP growth projected at 4.5%1 for the year, provided firm support to overall traffic demand.

Buoyed by robust business and consumer activity, the region’s airlines recorded a 7.1% year-on-year increase in the number of international passengers carried, reaching a combined total of 30.9 million in September.
Passenger demand, as measured in revenue passenger kilometres (RPK), rose by 6.7% year-on-year, matching the expansion in available seat capacity. As a result, the international passenger load factor averaged 80.7% for the month, remaining elevated amid ongoing supply chain constraints.
Meanwhile, air cargo markets remained strong, supported by shifts in Asian cargo flows following the implementation of U.S. tariffs. International air cargo demand, measured in freight tonne kilometres (FTK), grew by 5.0% compared with the same month last year. Offered freight capacity increased by 4.4% year-on-year, leading to a marginal 0.3 percentage point increase in the average international freight load factor to 60.8%.
Commenting on the results, AAPA Director General, Subhas Menon said: “Despite heightened trade tensions and the implementation of US tariffs, Asian economies have remained resilient, aided by the front-loading of exports, ongoing regional supply-chain realignments and firm domestic demand. Against this backdrop, Asia Pacific carriers posted a solid 10% increase in international passengers to a total of 289 million for the first nine months of the year, alongside a 7% year-on-year growth in international air cargo demand.”
Menon added: “The outlook for both international air passenger and air cargo markets remains positive. Asia Pacific carriers are well-placed to respond to demand growth, while navigating multiple challenges, including supply chain constraints as well as rising operational costs.”
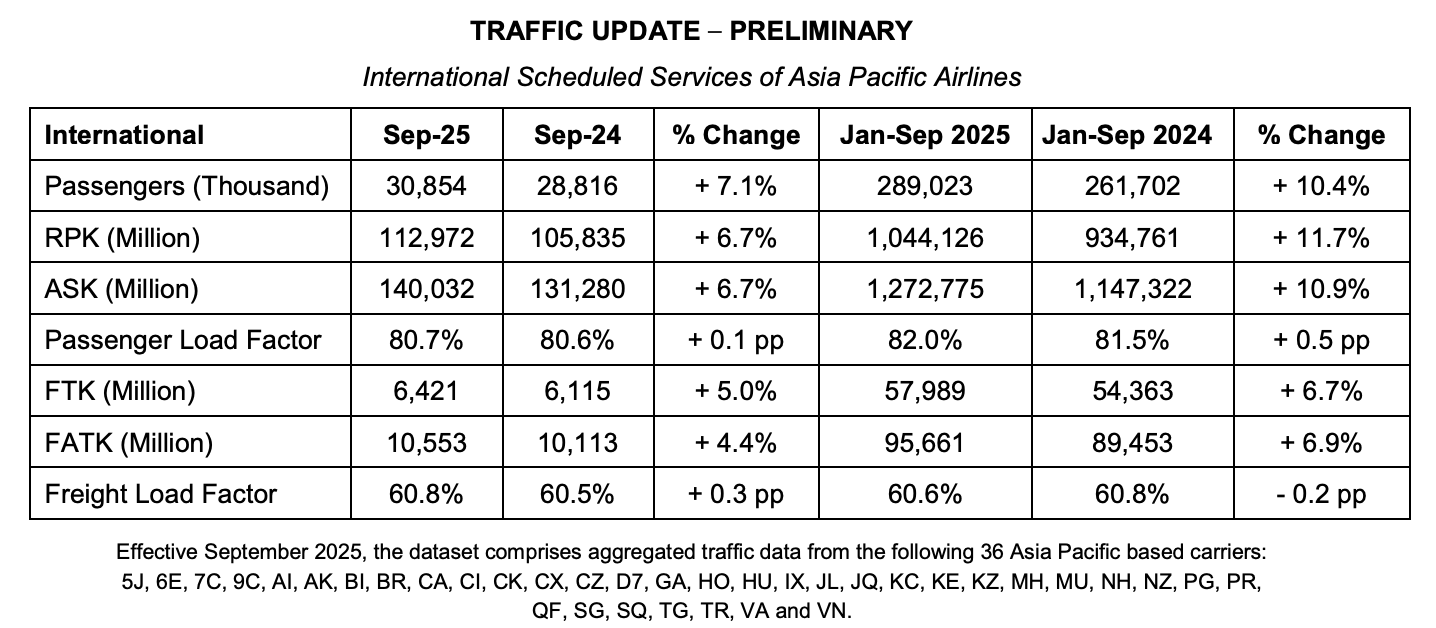
(Source: APPA)






